In the world of CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining, precision and control are paramount. As technology evolves, the need for efficient, flexible, and powerful control systems is more critical than ever. This is where Mach4, a popular CNC controller software, steps in. Mach4 brings a high degree of customization and control, providing users with the tools they need to manage even the most complex CNC machines.
Alongside Mach4, there are several important elements you need to understand in order to fully leverage its power. Whether you’re just starting out or looking to improve your CNC setup, this guide will walk you through four crucial topics that will help you maximize the potential of your system:
Mach4 CNC Controller – the heart of your CNC system, responsible for managing machine functions and ensuring smooth operations.
PoKeys Tutorial – a practical guide to integrating PoKeys devices with your CNC system to expand its capabilities and streamline control.
Mach 4 Motion Controller – a deep dive into motion controllers, which play a crucial role in ensuring precise movement and performance of your CNC machine.
Mach4 Probing – an essential feature for accurate measurement and alignment during machining processes.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore each of these topics in detail, explain how they are interconnected, and provide you with the knowledge needed to enhance your CNC machining experience. Whether you’re upgrading your setup or learning the ropes, this article will offer insights and tutorials that will improve your workflow and precision.
Let’s get started!
Understanding the Mach4 CNC Controller
The Mach4 CNC controller is the core software that powers and manages your CNC machine, enabling it to execute complex movements with precision and efficiency. Unlike its predecessor, Mach3, the Mach4 CNC controller was designed to offer better stability, scalability, and customization. It can handle a wide range of machine types, from simple mills and lathes to more advanced machines with multiple axes.
One of the primary advantages of the Mach4 CNC controller is its modularity. It is built in such a way that users can easily add or remove features depending on their specific needs. This flexibility is critical because it allows users to optimize their CNC setup for their unique manufacturing process, without being constrained by unnecessary features. This means whether you’re running a small workshop or a full-scale manufacturing facility, the Mach4 CNC controller can be adapted to suit your needs.
Key Features of Mach4 CNC Controller
- Modularity – As mentioned, Mach4 CNC controller‘s modular design allows users to pick and choose which features they need. Whether it’s toolpathing, probing, or motion control, you can customize the interface to ensure it fits your workflow perfectly.
- Improved Stability – One of the key improvements over Mach3 is the stability and reliability of Mach4. It is capable of managing large amounts of data and complex operations without freezing or crashing, making it ideal for advanced CNC operations.
- Motion Planning – Mach4’s advanced motion planning algorithm allows for smooth and accurate control of the CNC machine’s movements. The software calculates toolpaths efficiently, reducing errors and improving the quality of your finished product.
- Multi-Axis Support – The Mach4 CNC controller can control machines with multiple axes, making it perfect for advanced CNC systems, including 3D routing, laser cutting, and plasma machines. Whether you’re working with three-axis, five-axis, or more, Mach4 can handle the task.
- Customizability – The ability to create custom scripts using Lua programming language is one of the standout features of the Mach4 CNC controller. This allows advanced users to develop custom macros, automate tasks, or tailor the interface to their specific needs.
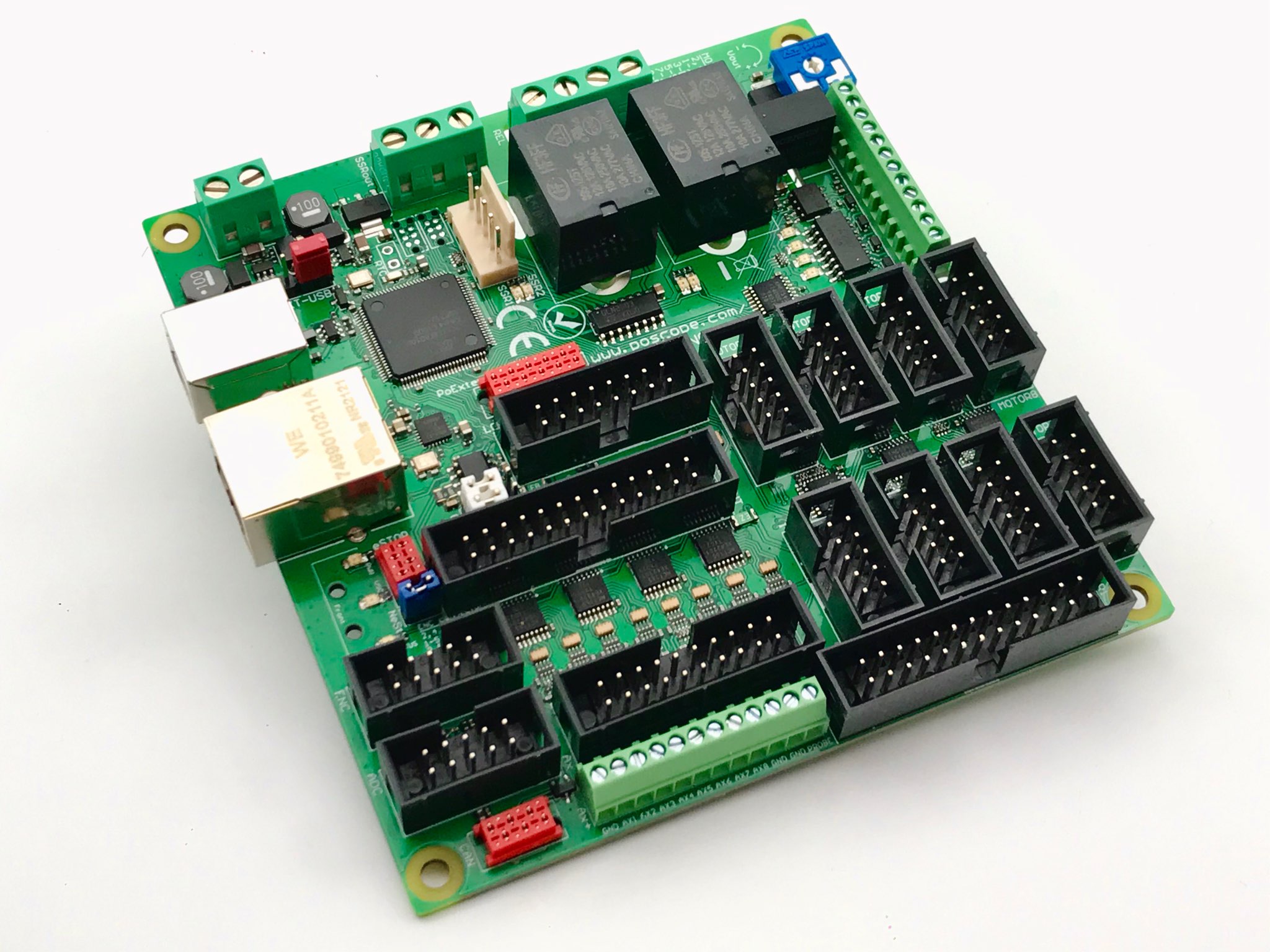
Integration and Compatibility
Another key reason why the Mach4 CNC controller is so widely adopted is its compatibility with various hardware and motion controllers. Whether you’re using an Ethernet-based motion controller or a USB-based one, Mach4 integrates seamlessly with them, ensuring that your CNC machine operates smoothly and with minimal latency.
Users will also appreciate that the Mach4 CNC controller works across different operating systems. While it is most commonly associated with Windows, its compatibility extends to other environments, offering flexibility for a wider range of users.
Benefits for Machinists and Hobbyists
For both professional machinists and hobbyists, the Mach4 CNC controller offers a plethora of benefits. Professionals appreciate its advanced functionality, stability, and precision, while hobbyists enjoy the ease of customization and user-friendly interface. Mach4 caters to users at different skill levels, allowing even beginners to get started quickly without sacrificing the advanced features that professionals need.
In conclusion, the Mach4 CNC controller stands out as a powerful and flexible solution for managing CNC machines. Its ability to integrate with various hardware, handle complex operations, and offer customization makes it a versatile choice for anyone serious about CNC machining. In the next chapter, we’ll explore how the PoKeys device can further enhance your Mach4 setup, improving control and functionality.
PoKeys Tutorial – Enhancing Your CNC Setup
Integrating a PoKeys device into your CNC system can significantly improve your machine’s capabilities. PoKeys is a multifunctional device used for connecting your CNC machine to external control systems, allowing for expanded input and output options. In this chapter, we’ll walk you through the basics of how to set up and use PoKeys with your CNC system, specifically in combination with the Mach4 CNC controller.
PoKeys devices are incredibly versatile, providing support for a wide range of applications. From basic motion control to advanced automation, these devices give users the power to fully customize their CNC setup. Whether you’re looking to add manual control panels, expand your input/output capacity, or enhance machine monitoring, PoKeys devices can be a game-changer.
What is PoKeys?
At its core, PoKeys is a USB and Ethernet interface device designed to connect PCs to various sensors, switches, and motor drivers. It serves as a communication bridge between your CNC machine and Mach4, allowing for better control and interaction. This makes it possible to control your machine via external inputs such as buttons, knobs, or even a touchscreen.
The main appeal of PoKeys devices is their ability to interface seamlessly with Mach4. They provide a large number of input/output (I/O) pins that can be configured for different purposes. For example, you can use PoKeys to connect a jog wheel or buttons for manual machine control, monitor sensor readings, or trigger specific machine operations based on external inputs. With a PoKeys device, you can expand the functionality of your CNC system far beyond its default settings.
Setting Up PoKeys with Mach4
Setting up a PoKeys device with your Mach4 CNC controller is relatively straightforward. Below is a step-by-step PoKeys tutorial to guide you through the process:
Install the PoKeys Software: Begin by downloading and installing the PoKeys configuration software from the official website. This software will help you configure the device, assign functions to each I/O pin, and ensure compatibility with Mach4.
Connect PoKeys to Your PC: Using either a USB cable or an Ethernet connection, connect the PoKeys device to your PC. Ethernet is generally preferred for better speed and stability, especially if you’re managing complex CNC systems.7
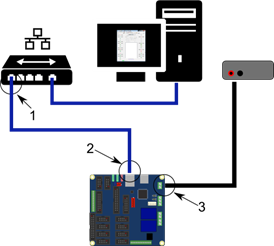
Configure PoKeys I/O: Launch the PoKeys configuration software and start assigning specific functions to each I/O pin. For example, you could assign pins to control a jog wheel, limit switches, or even an emergency stop button. PoKeys provides a wide range of configuration options to meet your specific needs.
Integrate with Mach4: Once the PoKeys I/O is set up, you’ll need to configure Mach4 to recognize and communicate with the device. Mach4 comes with a PoKeys plugin, which makes this process much simpler. Open Mach4, navigate to the “Configure” tab, and install the PoKeys plugin. From there, Mach4 will be able to interface with your PoKeys device.
Test and Fine-Tune: After setup, it’s crucial to test your system to ensure everything is working correctly. Use Mach4’s interface to jog the machine, test the I/O connections, and confirm that your buttons or sensors respond as expected. Fine-tune any settings in the PoKeys software or Mach4 plugin as needed to achieve optimal performance.
Practical Applications of PoKeys in CNC Systems
The possibilities for integrating PoKeys into your CNC system are vast. Here are some common applications where PoKeys devices can enhance your machine’s functionality:
- Jogging Control: One of the most popular uses of PoKeys is adding manual jogging control. This allows you to move the machine’s axes using a handheld device, such as a jog wheel or a joystick, giving you better control for precise positioning.
- Control Panels: Many machinists build custom control panels using PoKeys, adding physical buttons and switches for essential functions like start, stop, pause, and emergency stop. This offers a more intuitive and hands-on approach to machine operation.
- Sensor Integration: PoKeys devices support a variety of sensors, from temperature and pressure sensors to limit switches and proximity sensors. This allows you to monitor machine conditions and automate responses based on sensor data.
- Advanced Automation: For more complex operations, PoKeys can be used to control relays, stepper motors, or even solenoids. This opens the door to advanced automation techniques, such as tool changers or robotic arms.
Benefits of Using PoKeys with Mach4
Integrating a PoKeys device into your Mach4 CNC setup offers numerous benefits, including:
Increased I/O Capacity: PoKeys devices provide a large number of inputs and outputs, allowing you to add more controls, sensors, and devices to your CNC system.
Real-Time Control: With PoKeys, you can implement real-time controls, such as jogging or emergency stop, to enhance both safety and precision during operations.
Customization: Whether you’re building a custom control panel or integrating unique sensors, PoKeys gives you the flexibility to tailor your CNC machine to your specific needs.
Incorporating PoKeys into your CNC setup can greatly expand your machine’s capabilities and make operation more efficient and customizable. Whether you’re adding new input devices, improving real-time control, or enhancing automation, this versatile interface device allows you to take full advantage of what Mach4 has to offer. In the next chapter, we’ll explore Mach 4 motion controllers, another critical component of CNC machines that works hand in hand with both Mach4 and PoKeys for optimal performance.
Mach 4 Motion Controller – Precision and Control
The Mach 4 motion controller is a crucial piece of hardware that serves as the intermediary between your computer running Mach4 software and the CNC machine itself. It is responsible for executing the commands sent from the software to the machine, ensuring precise and synchronized movements. In this chapter, we’ll explore the role of the Mach 4 motion controller, how it works, and why it’s essential for smooth CNC operations.
What is a Mach 4 Motion Controller?
A Mach 4 motion controller is essentially a hardware device that converts the motion planning data generated by the Mach4 CNC controller software into signals that the machine’s motors can understand. These signals are what drive the machine’s various axes, ensuring that they move according to the planned toolpath with high accuracy and precision. Motion controllers come in different forms, typically connected via USB or Ethernet, and they are designed to handle the high-speed processing required for real-time CNC operations.
Unlike older parallel port setups that were often limited in speed and capability, modern Mach 4 motion controllers provide faster and more stable communication, allowing for complex and high-performance machining processes. They manage everything from spindle control to multi-axis movement, all while maintaining synchronization between the hardware and software.
Key Features of a Mach 4 Motion Controller
- Real-Time Communication – One of the primary functions of a Mach 4 motion controller is to enable real-time communication between the CNC machine and the Mach4 software. This ensures that commands are executed instantaneously and accurately, without delays or missed signals. This is especially important when working with high-speed machines or complex operations that involve multiple axes.
- Increased Processing Speed – The Mach 4 motion controller significantly improves processing speed compared to traditional parallel port systems. This speed boost means that more data can be processed in less time, resulting in smoother motion and higher-quality finishes. The controller can handle a large number of pulses per second, ensuring that even the most detailed toolpaths are executed with precision.
- Multi-Axis Support – Whether your CNC machine has two axes or five, the Mach 4 motion controller can support multi-axis setups with ease. This is essential for advanced machining operations like 3D routing, where precise coordination between different axes is critical. The controller ensures that each axis moves in perfect harmony, reducing the risk of errors and improving overall accuracy.
- Enhanced Stability – Another benefit of using a Mach 4 motion controller is its ability to enhance the stability of your CNC machine. Because it offloads much of the real-time processing from the computer to the hardware, the controller ensures that the system runs smoothly, even during long or complex jobs. This stability is particularly important in industrial settings, where downtime can be costly.
- Synchronization with Mach4 Software – The Mach 4 motion controller is specifically designed to work seamlessly with the Mach4 CNC software. The integration between the two ensures that motion commands are sent in real-time and that there is no lag or desynchronization between what the software is instructing and what the machine is doing.
Types of Mach 4 Motion Controllers
There are various types of Mach 4 motion controllers, each designed for specific use cases and hardware setups. Some of the most common types include:
- Ethernet Motion Controllers: Ethernet-based controllers are often preferred for their speed and stability. They can handle large amounts of data and offer fast, reliable communication between the CNC machine and the software. Examples include popular controllers like the ESS (Ethernet SmoothStepper).
- USB Motion Controllers: USB-based motion controllers are more accessible for hobbyists and small workshops, offering a simpler and more affordable setup. However, they are often limited in speed compared to Ethernet controllers and may not be suitable for very high-performance machines.
- PCI Motion Controllers: These are less common but can provide a robust solution for industrial applications where extreme precision and stability are required.
The choice of a Mach 4 motion controller depends on the specific needs of your CNC system. For instance, if you’re running a multi-axis machine with high-speed requirements, an Ethernet controller would likely offer the best performance. For simpler systems, a USB controller might suffice.
How the Mach 4 Motion Controller Improves CNC Performance
The Mach 4 motion controller plays a pivotal role in enhancing the performance of your CNC machine. Here are some of the ways it does so:
- Smooth and Accurate Movements: The motion controller ensures that all movements are executed smoothly and with high precision, even at high speeds. This results in cleaner cuts, more accurate toolpaths, and better overall quality of the finished product.
- High-Speed Machining: For operations that require rapid movements, such as plasma cutting or high-speed milling, the Mach 4 motion controller is able to process large amounts of data quickly, ensuring that the machine operates at its full potential without lag or slowdown.
- Reduced Error Rates: By managing the communication between the software and machine, the motion controller reduces the likelihood of missed steps, errors, or signal delays that can lead to inaccurate cuts or wasted material.
- Multi-Tasking Capabilities: A Mach 4 motion controller is capable of handling multiple processes simultaneously, such as controlling the spindle speed, managing axis movements, and monitoring sensor inputs all at once. This is particularly useful in complex CNC operations where timing and precision are critical.
Choosing the Right Mach 4 Motion Controller
When selecting a Mach 4 motion controller, it’s essential to consider your CNC machine’s specifications and the type of work you’ll be performing. Here are a few factors to keep in mind:
- Connection Type: As mentioned earlier, Ethernet controllers are generally faster and more reliable, while USB controllers are easier to set up. Choose based on the complexity of your machine and the level of performance you require.
- Number of Axes: Ensure the motion controller supports the number of axes in your CNC machine. If you’re running a multi-axis machine, make sure the controller can handle the synchronization and precision needed for smooth operation.
- Budget: Motion controllers vary widely in price, with higher-end models offering more features and better performance. Hobbyists or small shops might find USB controllers sufficient, while larger operations might benefit from the investment in an Ethernet controller.
The Mach 4 motion controller is an indispensable component of a CNC machine, translating software commands into precise mechanical movements. It enhances speed, accuracy, and stability, ensuring that your machine operates smoothly even during complex tasks. Whether you’re a professional machinist or a hobbyist, investing in a high-quality Mach 4 motion controller will significantly improve your CNC system’s overall performance.
In the next chapter, we’ll explore Mach4 probing, another critical aspect of CNC operations that allows for precise alignment and measurement, ensuring that your machine delivers accurate results every time.
Read also:
- The Evolution of CNC Systems: Understanding Ethernet I/O Controllers, Mach4 CNC Controllers, Mach4 Lasers, and CNC Wiring
- Enhancing CNC Machining Efficiency: Exploring USB I/O Controllers, Smart Relays, Mach4 Probing, and CNC Tool Setters
- Optimizing Your Model Railway Station: A Guide to Mach4 CNC Controllers, Stepper Motor Current, and Flat Cable Cutters
Mach4 Probing – Precision Measurement and Alignment
Mach4 probing is an essential feature in CNC machining that allows for precise measurement, alignment, and detection of workpieces. Probing helps machinists establish the exact position of the material on the CNC bed, ensuring accurate cuts, reducing setup times, and minimizing errors. In this chapter, we will explore how Mach4 probing works, its benefits, and how to set it up effectively to enhance your CNC machine’s performance.
What is Mach4 Probing?
At its core, Mach4 probing involves using a probe—a specialized tool that detects the surface of a workpiece and sends signals to the CNC controller to define its position. This can be extremely useful for various applications such as finding the exact center of a part, detecting edges, or aligning multiple pieces in a precise configuration. Once the probe makes contact with the workpiece, the Mach4 CNC controller records the exact coordinates, allowing you to set your work coordinates (also known as the machine’s zero point) accurately.
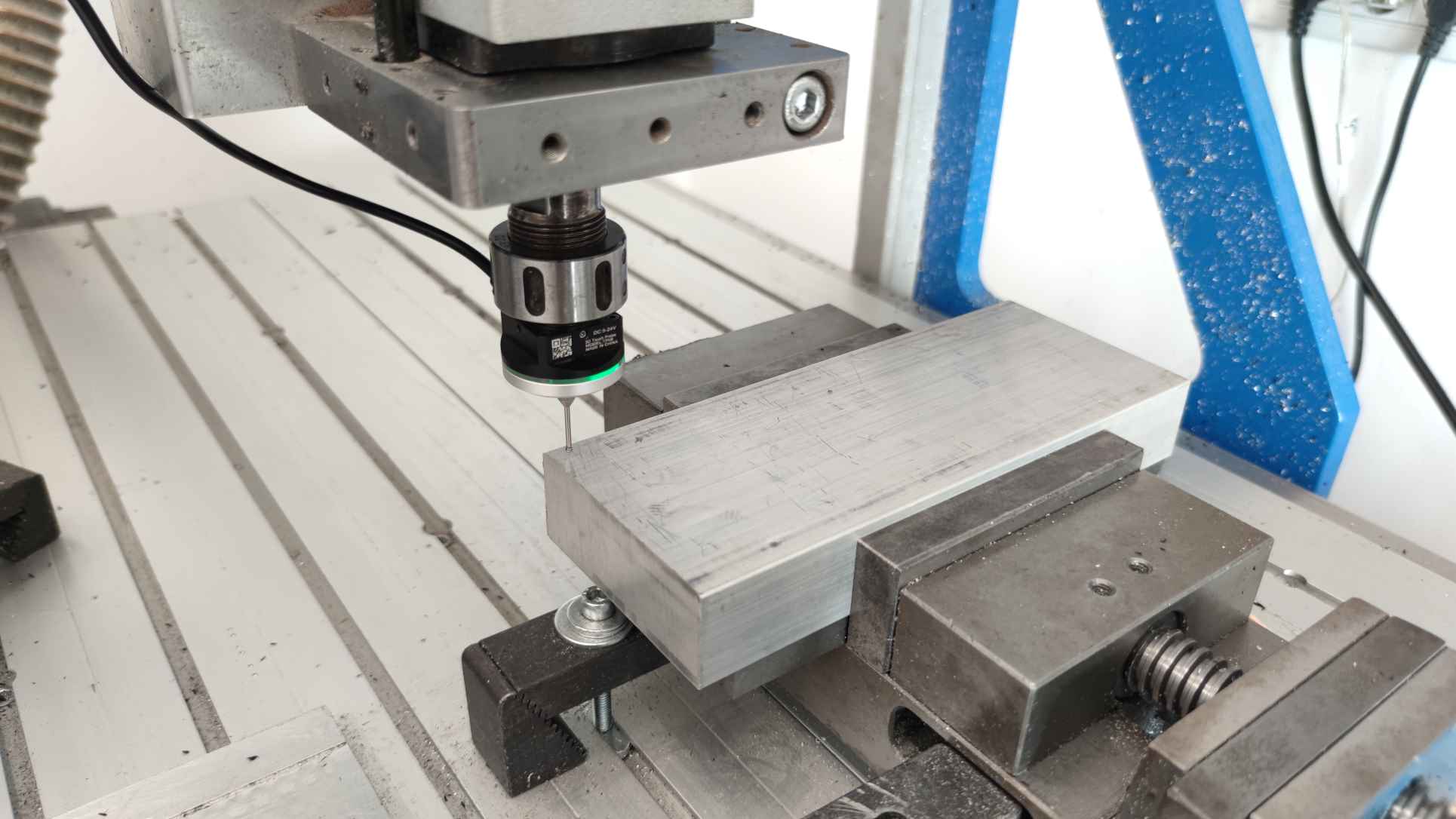

Probing is a valuable tool in the CNC machining process, as it ensures that the material is correctly positioned before the machining process begins. This minimizes the risk of costly mistakes caused by misalignment, such as uneven cuts or wasted materials.
Key Features of Mach4 Probing
- Accurate Workpiece Alignment: One of the main functions of Mach4 probing is ensuring that the workpiece is positioned correctly on the CNC machine’s bed. The probing tool touches off the surface of the material to precisely locate its edges, corners, or center. This eliminates guesswork and ensures that your toolpath aligns perfectly with the material, resulting in precise cuts.
- Touch Probe Integration: Mach4 probing supports various types of touch probes, including wired and wireless models. A touch probe is a precision device mounted on the machine’s spindle or tool holder, and when it comes into contact with the workpiece, it sends a signal to the CNC controller. This signal tells the software where the tool has touched the surface, helping to map out the workpiece’s position accurately.
- Automated Probing Cycles: One of the powerful features of Mach4 probing is the ability to automate probing routines. Mach4 supports a range of predefined probing cycles that allow for fast and easy setup. For example, there are cycles for edge detection, center finding, and surface mapping, all of which can be executed with minimal user input. This saves time and ensures consistency in part setup.
- Customizable Probing Scripts: Advanced users can take advantage of Mach4’s customizable probing scripts written in Lua, the same language used for other customizations in Mach4. By modifying or creating custom probing macros, you can tailor the probing process to your exact needs, optimizing workflows for specific tasks.
- Multiple Probing Modes: Mach4 supports different probing modes, including single-point and continuous probing. Single-point probing is useful for tasks like edge detection or tool setting, where the probe touches off a single point on the workpiece. Continuous probing, on the other hand, is used for surface mapping, where the probe continuously tracks the surface of the material to create a detailed profile.
Setting Up Mach4 Probing
Setting up Mach4 probing is relatively straightforward but requires careful attention to detail to ensure accurate results. Here’s a general guide to get you started:
- Install the Probe: First, install the touch probe in your CNC machine. This can be a wired or wireless probe, depending on your setup. Ensure that the probe is securely mounted in the spindle or tool holder.
- Configure Mach4 for Probing: In the Mach4 software, navigate to the probing setup menu. Here, you will need to define the type of probe you’re using and calibrate it. Calibration involves setting the probe’s offset (the difference between the probe tip and the spindle’s centerline), so the software knows exactly where the probe is relative to the tool.
- Define Probing Macros: Mach4 comes with several pre-configured probing macros for common tasks such as edge finding, corner finding, and tool height setting. You can select and customize these macros to fit your specific probing needs. For more advanced tasks, you can write custom Lua scripts to further enhance the probing capabilities.
- Run a Test Cycle: After setting up the probe, run a test probing cycle to ensure everything is working correctly. You can use a simple edge-finding routine to verify that the machine records the correct position when the probe makes contact with the workpiece. Ensure that the probe is functioning accurately before proceeding with actual machining.
- Incorporate Probing into Workflow: Once your Mach4 probing is set up and calibrated, you can incorporate it into your regular machining workflow. For example, you might use a probing cycle to detect the workpiece’s position at the start of each job, ensuring that every toolpath is aligned perfectly with the material.
Practical Applications of Mach4 Probing
Mach4 probing can be used in a wide range of CNC machining tasks, helping to increase accuracy and reduce setup times. Here are some common applications:
- Tool Height Setting: Using a touch probe to set the tool’s height is a quick and reliable way to ensure the cutting tool is at the correct depth. This is especially useful when switching between different tools during a single job.
- Edge and Center Finding: Probing is often used to detect the exact location of the material’s edges or center. This is essential when working with irregularly shaped parts or when precise alignment is required for tasks like engraving or drilling.
- Surface Mapping: For complex surfaces, Mach4 probing can be used to map the material’s topography. This is particularly useful for 3D milling or engraving, where slight variations in material height need to be accounted for to maintain consistent cut depth.
- Workpiece Alignment: By using probing cycles to detect the position and orientation of the workpiece, you can ensure that every job starts with the material perfectly aligned. This reduces errors and increases the consistency of your finished products.
Benefits of Mach4 Probing
Mach4 probing offers several benefits that can significantly enhance the precision and efficiency of your CNC operations:
- Reduced Setup Time: Probing eliminates much of the manual work involved in positioning and aligning the material. Automated probing routines can be completed in seconds, saving valuable time and improving workflow efficiency.
- Increased Accuracy: By using a probe to detect the exact position of the workpiece, you can ensure that every cut is made in the correct location, reducing the risk of misalignment and material waste.
- Consistency: Once the probing process is set up, it can be repeated with precision across multiple parts. This consistency is essential for batch production and helps maintain uniform quality across all machined parts.
- Error Reduction: Probing helps to detect any errors in workpiece positioning before machining begins, reducing the likelihood of costly mistakes and rework.
Mach4 probing is a powerful feature that provides enhanced precision and efficiency in CNC machining. Whether you’re using it to align workpieces, find edges, or map complex surfaces, probing reduces setup time and ensures that your cuts are accurate and consistent. By incorporating Mach4 probing into your CNC workflow, you can improve the overall quality of your work while minimizing errors and downtime.
In the next section, we’ll summarize the key takeaways from the guide and emphasize the importance of using tools like the Mach4 CNC controller, PoKeys, motion controllers, and probing for a more efficient and precise CNC experience.
Read also:
- Mastering CNC Control: A Comprehensive Guide to Mach4, Mach3, USB Stepper Motor Controllers, and Stepper Motor Drivers
- Understanding Relay Modules: Smart Relay, Arduino Driving Relay, Raspberry Pi Relay, and 8-Channel Relay Modules
- Understanding the Core Components of Industrial Automation: Ethernet I/O Controllers, Modbus Stepper Drivers, Stepper Motor Currents, and Automation Control Devices
Bringing It All Together for Precision CNC Control
In the world of CNC machining, precision and control are paramount. Throughout this article, we’ve explored how key tools like the Mach4 CNC controller, PoKeys, Mach 4 motion controllers, and Mach4 probing work in harmony to enhance the capabilities of your CNC machine.
The Mach4 CNC controller serves as the software backbone, translating complex designs into machine instructions with unmatched flexibility and customization options. This powerful tool enables you to manage every aspect of your CNC system, from basic movements to advanced machining processes.
The PoKeys device further enhances this setup by expanding the input/output capabilities of your machine. Whether you’re adding manual control panels, sensors, or relays, PoKeys offers an efficient solution for improving the customization and automation of your CNC workflow. The integration with Mach4 ensures seamless communication and control, making it easier than ever to manage even the most complex tasks.
The Mach 4 motion controller is the critical hardware link that ensures your machine’s motors operate smoothly and accurately. With real-time communication and high-speed processing, this device handles everything from spindle control to multi-axis coordination. The result is smooth, precise movements and reduced errors, which are essential for producing high-quality machined parts.
Finally, Mach4 probing brings unparalleled accuracy to the setup and alignment process. Probing enables quick and precise detection of workpiece edges, centers, and surfaces, reducing setup times while improving overall precision. Whether you’re setting tool heights or aligning irregularly shaped materials, Mach4 probing ensures your CNC operations start on the right foot.
By combining these tools, you can achieve a level of precision, efficiency, and customization that is essential for both hobbyists and professionals in CNC machining. Each component—Mach4 CNC controller, PoKeys, Mach 4 motion controller, and Mach4 probing—contributes to a streamlined workflow, reducing errors, improving accuracy, and maximizing productivity.
In summary, mastering these tools allows you to take full control of your CNC machine, making it easier to handle complex tasks and ensuring consistently high-quality results. With the right combination of software and hardware, you can optimize your CNC machining processes, improving both efficiency and precision, and ultimately, the success of your projects.
